
What is Edge Computing and why should you pay attention to it?
The accelerated growth and technological advances of IoT devices are generating volumes of data that were previously unimaginable. These will continue to grow in the following years, and continue to multiply as mobile devices become connected to 5G networks.
From connected vehicles to intelligent robots in the industrial sector, the amount of data they generate is growing all the time, but most of it is not being exploited or used at all. Edge computing leverages it to provide valuable insights and predictive analytics in real-time, resulting in improved quality and expanded value.
Gartner estimates that by 2025, 75% of data will be processed outside of the traditional data center or cloud
This union will be crucial to the future of the smart industry and will have a major impact on all sectors, turning operations around and driving innovation. We’ll tell you all about it!
What is Edge Computing?
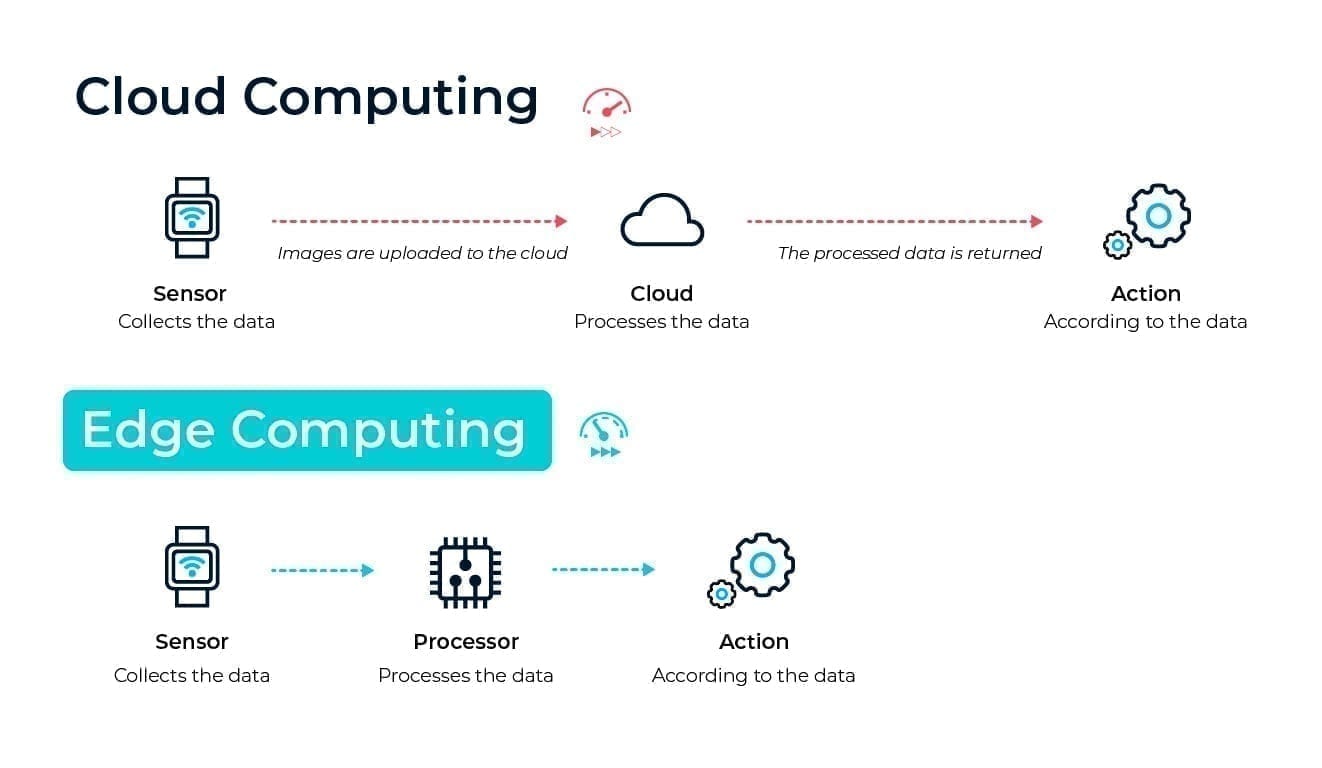
Edge computing is a distributed computing infrastructure in which IoT (Internet of Things) data is processed, from sensors, at the periphery of the network, at the same or as close as possible to the source that generates it.
As the name suggests, data processing is not done centrally in the cloud but is decentralized to the edge of the network.
Its scope and impact affect activities that require low latencies (the time it takes for information to go to the server and return), handle heavy data, or involve more interactivity and sensitivity to distance with network points. A clear example is the consumption of video content, especially on-demand, but it can be extrapolated to all kinds of sectors, such as factories, logistics, Smart Cities, IoT…
It is also essential for the development of Augmented Reality, where low latency maintains coordination between what is being done and what is being seen. Another example is smart cars, which will be connected to cameras and sensors that will capture information from the environment in real-time.
Edge Computing Benefits
The great advantage of Edge Computing is that it allows companies to save time and money since it analyzes data in real-time, which is essential in industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, or telecommunications. This increase in the speed of data analysis exponentially improves the internal processes of companies.
Furthermore, it addresses the centralization of services in a large data pool that cloud computing cannot adequately address. It focuses on several smaller computing sites that lower network costs, avoid bandwidth constraints, reduce transmission delays, ensure better security of sensitive data, reduce load times…
Another advantage is the ability to work in a dedicated environment, which guarantees the privacy of information and local management, without the need to deploy a complex infrastructure within the company.
Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing
The big difference between Edge and Cloud Computing is that the first one reduces energy consumption, bandwidth, and response time. But these are not the only advantages:
- Diversification: as IoT devices become more present in our daily lives, Edge Computing will become increasingly essential to prevent the system from collapsing.
- Cybersecurity: if we diversify the information on multiple devices, the data will be even more protected, and if an environment receives an attack, the damage will be minimal.
- Speed: because the data is processed as close to the place of origin as possible, the response is immediate.
However, the growth of Edge Computing should not be taken as the end of Cloud. Nothing could be further from the truth, as both technologies are heading towards a computing model in which they are presented as complements, or even as hybrids, to optimize processes according to needs.
The Cloud came at a time of need to reduce the use of hardware without sacrificing cybersecurity. Edge computing arrives in a world that is increasingly connected and where IoT is increasingly present, so its use enhances the cloud system and becomes an intermediary for a more intelligent, efficient, and secure use.
Edge Computing and IoT
As we have been discussing in previous points, Edge Computing and IoT are a great inseparable duo that will define the future of the fourth industrial revolution.
IoT devices receive and send data over networks without direct human intervention. This is where Edge Computing becomes essential because when these devices need real-time processing and transmission, they cannot suffer from lagging or connection problems. Edge Computing makes it possible to manage data in a more direct way, giving IoT devices a higher computational and processing capacity away from the Cloud.
Therefore, by bringing IoT devices and edge computing together, users and enterprises benefit from:
- Improved latency levels for transmitting data
- Improved user experiences
- Increased bandwidth
- Faster service speed
- Increased security
- Easier to achieve consumption trends thanks to data collection.
In addition, they reduce spending on Cloud services or the environmental footprint of using a data center.
Edge Computing and IoT Use Cases Examples
The speed at which information can be transmitted means that we can find examples of IoT and Edge Computing in many industrial sectors:
- In hospitals, sensors on the devices would collect patient data stored on local servers (which would increase the privacy of this sensitive information).
- Likewise, an edge computing framework in smart homes would reduce latency and potential cybersecurity issues.
- In autonomous vehicles, collecting data through their sensors allows one to know the state of traffic, pedestrians, or traffic lights and thus act quickly to avoid accidents.
- For small oil and gas plants with poor infrastructure for a centralized cloud, it helps to monitor and process data more efficiently.
Edge Computing and 5G
We can define 5G as the fifth generation of mobile communication, which will enable hyperconnection between a wide variety of devices that go beyond the cell phone or computer.
Although 5G is faster than 4G, the advantages it brings are useless if the content and applications are not brought closer to the place where they are consumed or executed. This is where Edge Computing comes in, processing this information at the place where they are generated, without the need to take them to the cloud over and over again. Both are transforming the way companies, governments and consumers interact and do business, and leading to revolutionary and innovative services.

5G brings a radical change in the connectivity of users and devices, providing higher capacity and speed, lower latency, higher reliability, more automation, flexibility, cost-effectiveness…
This translates into absolute immediacy and makes it possible to open up a world of applications that until now were unthinkable. The union of both technologies promotes an exponential change in the use of sensors, robots, intelligent energy…
Ultimately, Edge Computing solutions are intended to improve the experience of businesses and individual users, regardless of industry.
Edge Computing by industry
Many industries are joining this network modality, whether in the banking, mining, industrial, telecommunications, etc. Practically all companies are developing strategies designed to personalize customer experiences, to enliven actions and to allow them to be uninterrupted at all times.
Edge computing is allowing them to adopt a decentralized computing architecture on a massive scale, but each case needs a particular treatment: Cloud Edge, IoT Edge or Mobile Computing.
Thanks to the power of data, your business will be ready to face any challenge of the digital era. Edge Computing will completely change the way connected devices are designed, placing the processing power in an infrastructure with multiple intelligent systems. If you want to take advantage of this opportunity and join this revolution, we offer you the best experts to advise and guide you in a personalized way.




